In our increasingly connected world, the ability to reliably transmit high-fidelity data is more critical than ever. The backbone of modern telecommunications and fiber optic networks relies on pristine signal quality to function optimally. This is where innovative components like Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers come into play.
By precisely controlling the polarization of light, these devices ensure consistent and error-free data transmission across global communication networks.
Introducing Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers
Polarization effects have long been the bane of optical engineers, introducing distortions that degrade signal integrity. Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers overcome this by using specialized fibers and advanced filtering techniques to maintain consistent polarization alignment as light propagates through the system. The resulting enhancement in signal quality and stability unlocks the true potential of modern high-speed fiber optic networks.
How Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers Work
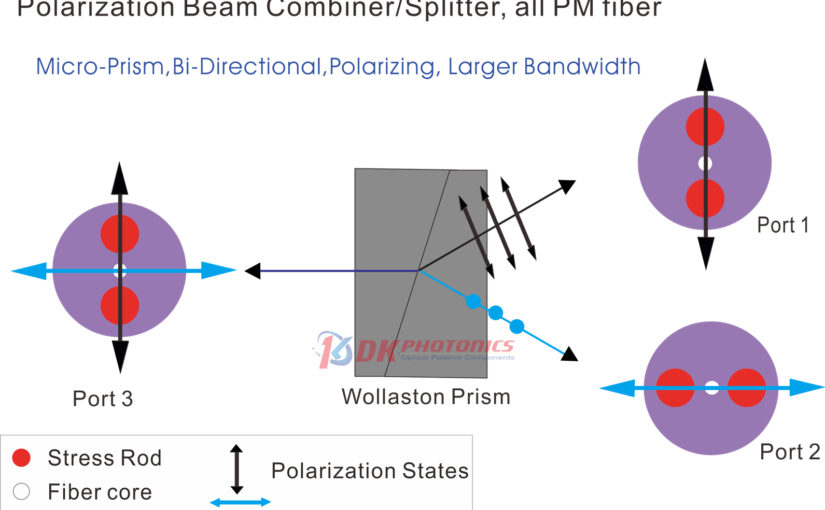
The inner workings of Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers leverage the polarization sensitivity of light. As an electromagnetic wave, light consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. The orientation of these fields defines the polarization state. Within optical fibers, factors like stress, bending, and temperature changes can randomly alter polarization, scattering the signal. Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers counteract this by coupling light selectively based on the polarization state.
This enables precise separation and processing of optical signals in systems like dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM), a key technology for expanding telecom network capacity. By assigning separate wavelengths to distinct polarization channels, vastly more information can be transmitted through a single fiber optic cable. Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers is crucial to extract and process each polarized wavelength channel independently.
Enhancement to Signal Integrity
As optical technologies progress, the underlying need for pristine signal quality persists. Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers answer this need with an elegant solution that leverages the very nature of light itself. Their unique ability to manipulate polarization states establishes them as an enabling technology across a diverse range of fields.
Applications across Industries
The telecommunications industry relies extensively on such polarization-splitting components. But the applications extend much further. Any field that utilizes laser systems can benefit from the signal-enhancing capabilities of Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers. From medical devices to industrial manufacturing, they optimize laser performance by ensuring a stable polarized output, free from disruptive polarization fluctuations.
Scientific research involving lasers also demands the precision that polarization-maintaining couplers offer. Applications like laser interferometry, nonlinear optics, and quantum computing often require intricate polarization control to conduct cutting-edge experiments. By stabilizing inherent polarization variability, these couplers enable groundbreaking research.
From powering global digital infrastructure to pushing the frontiers of scientific research, Polarization Maintaining Filter Couplers are indispensable components for the modern photonics engineer’s toolkit. Their capacity to enhance signal integrity empowers the realization of systems and applications limited only by imagination.