The IT refers to a medium where information is transmitted via a link. If two locations want to communicate with each other, one link is sufficient. To connect more locations more links are required What if only one link e.g. between two cities is available, but more applications shall be connected? Using the WDM technology, fiber optic links can be utilized for data transmission more efficiently.

The idea of xWDM technology
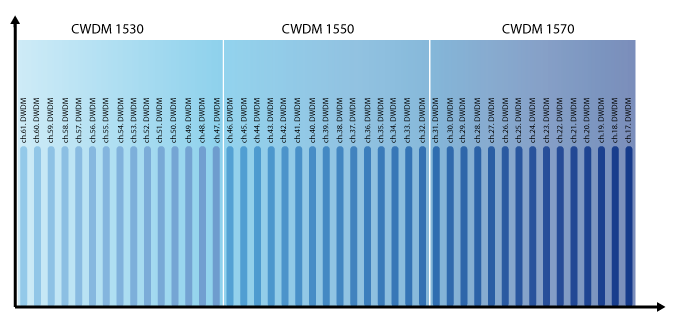
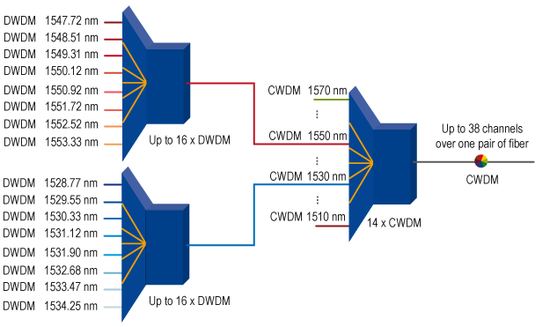
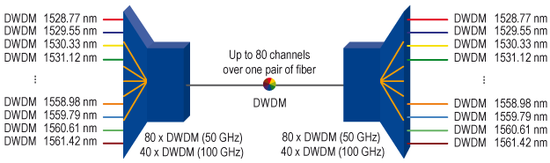
Each application is allocated to a dedicated color (wavelength) to communicate with a remote station. The advantage is that different colors can be simultaneously transmitted using one pair of fiber. For this purpose a multiplexer combines all different colors which will then be transmitted to the remote station over one pair of fiber. At the remote site the combined signal is separated again into different colors by a demultiplexer. Generally only one light beam with one wavelength is transferred over a pair of fiber. The wavelength multiplexing technology provides the ability to transmit more light beams, each having different wavelengths, using the same optical link. Due to the fact that wavelengths do not interfere, single light beams can be separated from each other using simple filters. A laser serves as the source of light and light-sensitive diode as receiver unit. Wavelength multiplexing is differentiated in CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technology. Advantage: With the use of WDM, it is possible today to transfer nearly 1 Tbps (C-band) via one pair of fiber.