In today’s world of intensive communication needs and requirements, “fiber optic cabling” has become a very popular phrase. In the field of telecommunications, data center connectivity and ,video transport, fiber optic cabling is highly desirable for today’s communication needs due to the enormous bandwidth availability, as well as reliability, minimal loss of data packets, low latency and increased security. Since the physical fiber optic cabling is expensive to implement for each individual service, using a Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) for expanding the capacity of the fiber to carry multiple client interfaces is a highly advisable. WDM is a technology that combines several streams of data/storage/video or voice protocols on the same physical fiber-optic cable by using several wavelengths (frequencies) of light with each frequency carrying a different type of data. With the use of optical amplifiers and the development of the OTN (Optical Transport Network) layer equipped with FEC (Forward Error Corection), the distance of the fiber optical communication can reach thousands of Kilometers without the need for regeneration sites.
DWDM vs. CWDM
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) is a technology allowing high throughput capacity over longer distances commonly ranging between 44-88 channels/wavelengths and transferring data rates from 100Mbps up to 100Gbps per wavelength. Each wavelength can transparently carry wide range of services such as FE/1/10/40/100GBE, OTU2/OTU3/OTU4, 1/2/4/8/10/16GB FC,STM1/4/16/64, OC3/OC12/OC48/OC-192, HD/SD-SDI and CPRI. The channel spacing of the DWDM solution is defined by the ITU.xxx (ask Omri) standard and can range from 25Ghz, 50GHz and 100GHz which is the most widely used today. Figure – 1 shows a DWDM spectral view of 88ch with 50GHz spacing.
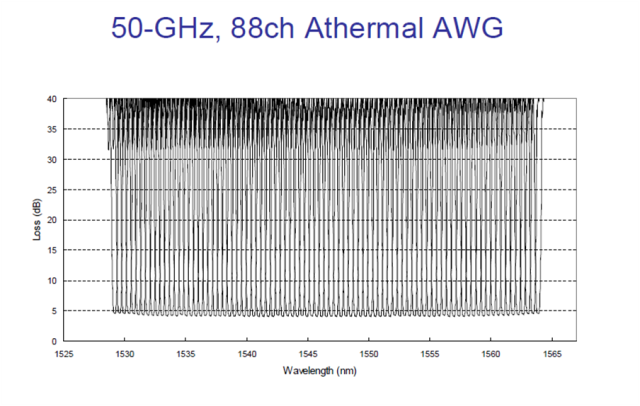
Figure -1: Spectral view of 50GHz spacing 88 DWDM channels/wavelengths
DWDM systems can provide up to 96 wavelengths (at 50GHz) of mixed service types, and can transport to distances up to 3000km by deploying amplifiers, as demonstrated in figure 2) and dispersion compensators thus increasing the fiber capacity by a factor of x100. Due to its more precise and stabilized lasers, the DWDM technology tends to be more expensive at the sub-10G rates, but is a more appropriate solution and is dominating for 10G service rates and above providing large capacity data transport and connectivity over long distances at affordable costs. The DWDM solution today is often embedded with ROADM (Reconfigurable Optical Add Drop Multiplexer) which enables the building of flexible remotely managed infrastructure in which any wavelength can be added or dropped at any site. An example of DWDM equipment is well demonstrated by PL-1000, PL-1000GM, PL-1000GT, PL-1000RO, PL-2000 and PL-1000TN by DK Photonics Networks.

Figure-2 Optical amplifier used in DWDM solution to overcome fiber attenuation and increase distance
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) proves to be the initial entry point for many organizations due to its lower cost. Each CWDM wavelength typically supports up to 2.5Gbps and can be expanded to 10Gbps support. This transfer rate is sufficient to support GbE, Fast Ethernet or 1/2/4/8/10G FC, STM-1/STM-4/STM-16 / OC3/OC12/OC48, as well as other protocols. The CWDM is limited to 16 wavelengths and is typically deployed at networks up to 80Km since optical amplifiers cannot be used due to the large spacing between channels. An example of this equipment is well demonstrated by PL-400, PL-1000E and PL-2000 by DK Photonics Networks.
It is important to note that the entire suite of DK Photonics’ equipment is designed to support both DWDM and CWDM technology by using standards based pluggable optical modules such as SFP, XFP and SFP+. The technology used is carefully calculated per project and according to customer requirements of distance, capacity, attenuation and future needs. DK Photonics also provides migration path from CWDM to DWDM enabling low entry cost and future expansion that can be viewed in the DWDM over CWDM technology page
WDM Installation
For designing and implementing a WDM network, there is a need to know some basic information regarding the infrastructure such as fiber type, attenuation of fiber, distance of fiber, network topology, service type, rate and connectivity. Based on this information, calculation of the optical link budget, OSNR (Optical Signal Noise Ratio) and dispersion can be performed in order to provide reliable, error free layer-1 optical solution.
DK Photonics’ WDM diversified equipment portfolio can provide either CWDM or DWDM solution for 4 wavelengths or 88 wavelengths ranging from few km to thousands of km and fit to the exact customer network needs. The network can be a point-to-point, linear add/Drop or ring Topology with passive Mux/DeMux or ROADM based infrastructure.
The WDM equipment serves as a demarcation point and is installed behind the Ethernet switch, router fiber channel SAN Fabric or SDH/SONET ADM coloring the fiber into different spectral wavelengths and multiplexing the rates fully isolated from each other over the same fiber to the remote site. This allows transmission of multiple channels of different services and rates of data over the same fiber utilizing the fiber resources agnostically to the service type and rate.
The WDM technology can be applied to multiple applications such as connecting building service agnostic optical layer backbone, data centers connectivity, Video broadcast, LTE fiber, cloud computing backbone, increasing existing fiber bandwidth and spectral efficiency.
Figure 3 shows the main traditional and emerging CWDM and DWDM technology applications which keep growing along with the rise of the cloud computing and CSP (Content Service Providers) as well as Smart phones and video applications causing constant increase to the WDM technology deployment and new capacities such as 100G.
Figure 3 – Main CWDM and DWDM technology applications
DK Photonics’ WDM products designed for easy and fast implementation take up minimal space and use least power, thus providing the highest integration level of CWDM and DWDM networks in the smallest 1U footprint, while providing high ROI. Additionally, the CWDM DWDM optical network is managed remotely with either DK Photonics’ Light Watch NMS/EMS or the imbedded web based management system as well as via any 3rd party SNMP tool.
Read more related articles :
Filter-based WDM CWDM Mini CWDM Module DWDM