Coarse wavelength division multiplexing (CWDM) is a wavelength multiplexing innovation for city and get to networks. Transmission is acknowledged utilizing 18 channels with wavelengths between 1270 nm and 1610 nm. Because of the channel separating of 20 nm financially savvy lasers can be utilized. The channel width itself is 13 nm. The rest of the 7 nm is intended to secure the space to the following channel. It is a technique for consolidating multiple signals on laser beams at different wavelengths for transmission along fiber optic cables, with the end goal that the quantity of channels is less than in dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) however more than in standard wavelength division multiplexing (WDM).
CWDM frameworks have channels at wavelengths divided 20 nanometers (nm) separated, contrasted and 0.4 nm dispersing for DWDM. This permits the utilization of minimal effort, uncooled lasers for CWDM. In a common CWDM framework, laser emissions happen on eight channels at eight characterized wavelengths: 1610 nm, 1590 nm, 1570 nm, 1550 nm, 1530 nm, 1510 nm, 1490 nm, and 1470 nm. However, up to 18 unique channels are permitted, with wavelengths ranging down to 1270 nm. The energy from the lasers in a CWDM framework is spread out over a larger range of wavelengths than is the energy from the lasers in a DWDM framework. The tolerance (degree of wavelength imprecision or variability) in a CWDM laser is up to ± 3 nm, while in a DWDM laser the tolerance is substantially more tightly. On account of the utilization of lasers with lower precision, a CWDM framework is more affordable and consumes less power than a DWDM framework. Be that as it may, the greatest realizable separation between nodes is littler with CWDM.
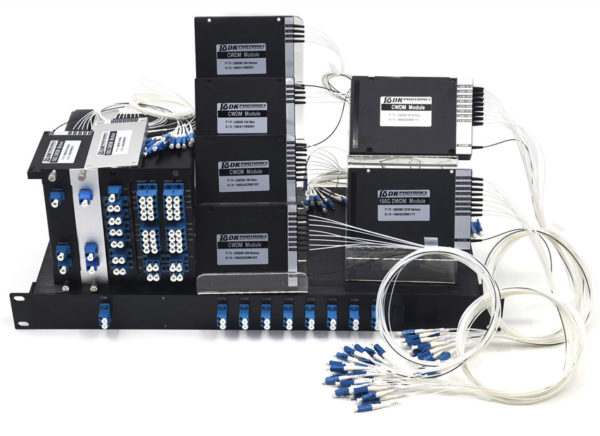
DK Photonics, the globally recognized manufacturer based in china can supply two primary configuration CWDM modules: CWDM multiplexer/demultiplexer (mux/demux) modules and CWDM add/drop multiplexer (OADM) modules.

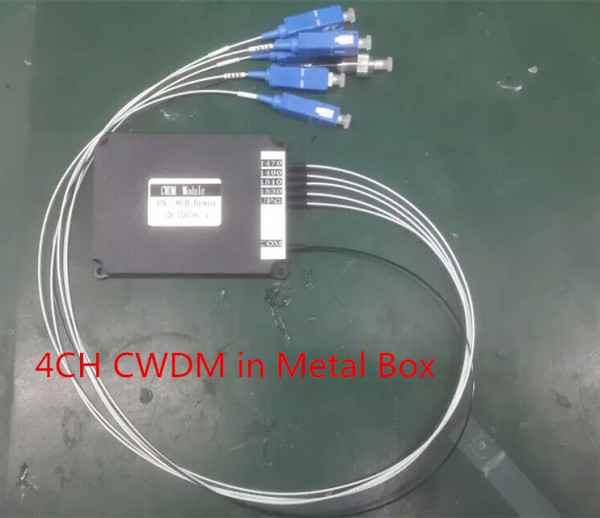
CWDM mux/demux modules are accessible in 4, 8 and 16 channel arrangements. These modules latently multiplex the optical signal yields from at least 4 electronic devices, send them over a single optical fiber and after that de-multiplex the signs into partitioned, unmistakable signals for contribution to electronic devices at the flip side of the fiber optic connection.
CWDM add/drop multiplexer modules give the capacity to include or drop a single wavelength or multi-wavelengths from a completely multiplexed optical signal. This enables middle of the road areas between remote locales to get to the normal, indicate point fiber segment linking them. Wavelengths not dropped go through the OADM and proceed toward the remote site. Extra chose wavelengths can be included or dropped by progressive OADMS as required.
There are a few organizations in market that are considered bosses at the designing and assembling of optical CWDM mux and demux module applications. One can contact these organizations to profit top notch items. Contact a provider today and get them!